Mass production Fin skiving machines with unlimited part length : PSF Series
PSF-Series Flat table type continue Fin Skiving Machine
Flat table continue fin skiving machine
3 SIZES : 140mm - 330 mm - 480 mm skiving width
Mass Production
Max Length = 6m
PSFS/PSFSB-Series Slant table type Flexible Fin Skiving Machine
Flexibility in FIN Skiving - Full step programmable
4 SIZES : 280mm - 330 mm - 380 mm - 580 mm skiving width
High precision cnc Production
Limited Lengths till 1600 mm single pass
PSFSB-350-HP High Precision Fin Skiving Machine
Super High precision CNC fin skiving machine
1 SIZE : 330 mm skiving width
max 800 mm Length
Skiving at 50µm fin thickness for certain super high precision applications
Prototype and high complex Fin skiving machines with exceptional flexibility: PSFS and PSFS-B Series
Full CNC complex skiving machines
Fin Skiving
In the skiving process, fins are machined using special tooling, whereby precisely sliced layers from an extruded metal block are bent at the base of the slice to form slender curved fins. Since the fins and base is an integral unit, the interface resistance seen in folded and bonded heat sinks is not present. This process was originally developed to manufacture sparse natural convection arrays, but recent efforts have been focused towards achieving tighter fin spacing, necessary for forced convection cooling.
Aluminum 6063 is the preferred material on account of its superior machinability and strength, but copper arrays can also be made. The depth of cut determines the fin thickness (T) and can be very low between 0.10 – 0.8mm, resulting in extremely thin fin structures, yielding light and competitive heat sink designs. The distance between fins can be shortened as much as 0.4mm and their height can reach 300mm. The ratio of height/thickness can reach easily around 250 times.
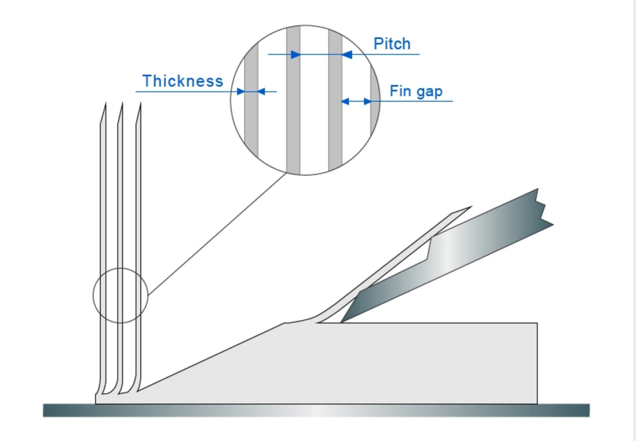
Production of skived heat sinks
Skiving heat sinks: When passing through the machine, slabs are skived in a specific angle so as to form and bend the fins. With the repetitive cutting, it forms consistent gaps and structures and can be used for cooling high-power devices under air-cooled conditions. This process can enhance 8~15% of the cooling capacity as compared to the stitched fin process. Leading the heat dissipation with innovation high density ,high performance, high aspect ratio, excellent performance. Skived heat sinks are produced using a sharp knive that, asit passes over the material, curl up a small thickness of metal which is then bent vertically to form the fin. Skived fins are produced from a bar of material and then cut to length as required by the final application. The final heat sink can be machined using normal fabrication techniques. Because of the thin fins, care must be taken in handling to prevent damage. It is suggested that a shroud be placed over the fins to help prevent damage.
Skived fin heat sinks: This process can enhance 8~15% of the cooling capacity as compared to the stitched fin process.
Skiving fin technology leading the heat innovation high density ,high performance, high aspect ratio, excellent performance.
How skived Fin heatsinks are made!
Skived heatsinks with optimal cooling capacity
Skived Fin Heat Sinks
Product Details Key Industries Related Products
Skived Fin Heat Sinks offer highly optimized cooling as they allow for higher fin densities than what is manufacturable using extrusion methodologies, but do not have an interface joint that restricts heat flow like bonded or brazed fin heat sinks. Unlike bonded or brazed heat sinks, Skived Fin Heat Sinks are constructed from a single piece of material and offer reduced thermal resistance since there is no joint between a base and fins. These heat sinks are manufactured by precisely slicing the top of the base, called skiving, folding it back to where it is perpendicular to the base, and repeating at regular intervals to create fins.
The skiving process enables high fin density and thin fin heat sink geometries for optimal thermal performance. By packing as much fin surface area into a given volume, skived fin heat sinks have greater heat transfer than other single piece construction heat sinks such as extruded aluminum heat sinks. Compared to extruded aluminum, skived fin heat sink fabrication does not rely on expensive tooling, providing greater design flexibility and faster prototyping. Instead, each fin is cut separately using the same tool which allows for lower tooling costs.
Skived heat sinks can be constructed of aluminum or copper allowing for full, one-piece copper solutions for high performance cooling.
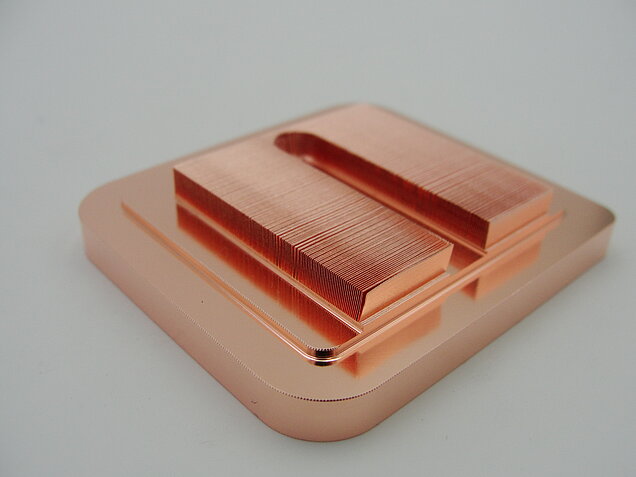


Skived Fin Heat Sinks
Skived Fin Heat Sink Types
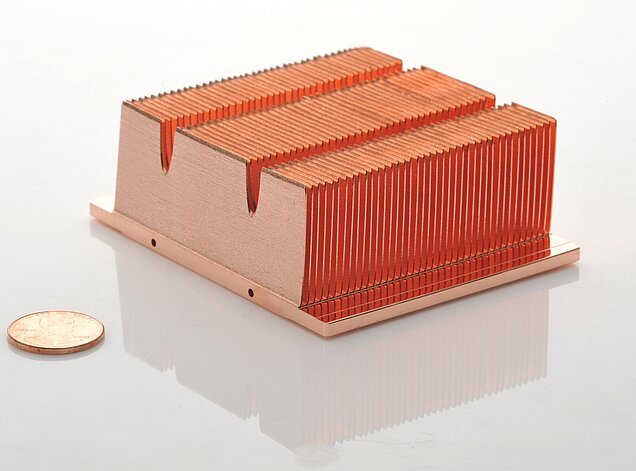
1. Copper Skived fin heatsink:
Copper thermal conductivity is good, plus the skived fin technology can achieve the maximum heat dissipation area per unit volume, greatly improve the overall heat dissipation performance. Copper skived fin heat sink is used in high end chip, cpu heat dissipation, server and other fields
High speed skiving of copper CPU heat sinks
Skiving of fins of 0,08 mm or smaller
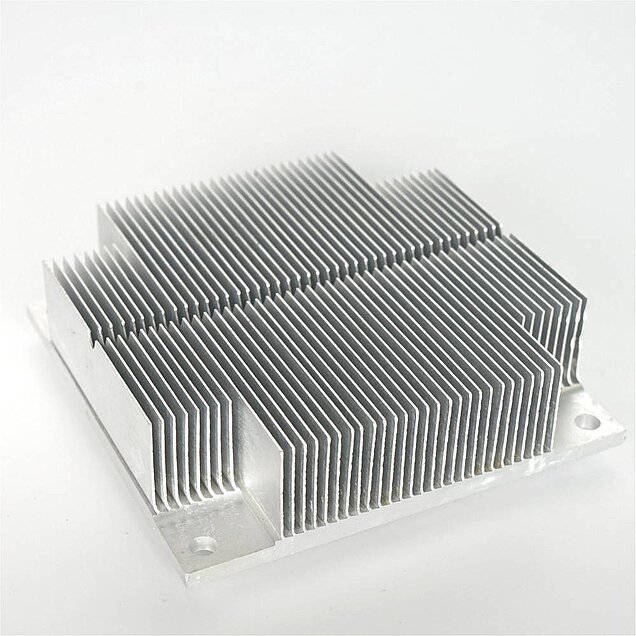
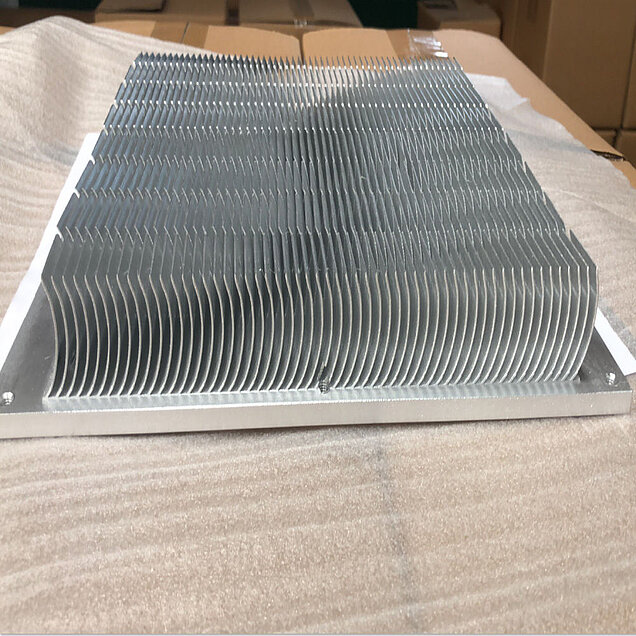


2. Aluminum skived fin heat sink:
Generally made of pure aluminum, thermal conductivity is higher than aluminum alloy, and with skiving technology, heat dissipation performance is more stable than aluminum extrusion heat sink. Aluminum skived heat sinks are widely used in photovoltaic industry, electric vehicles, inverters, led lights ,communication products and so on.
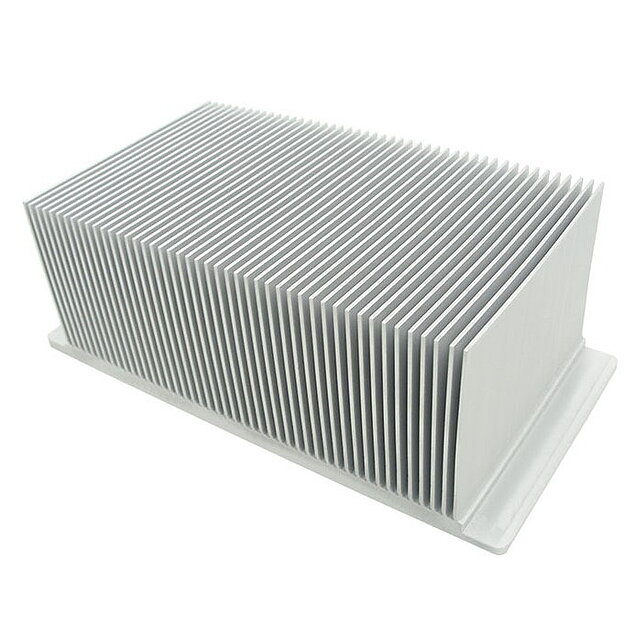
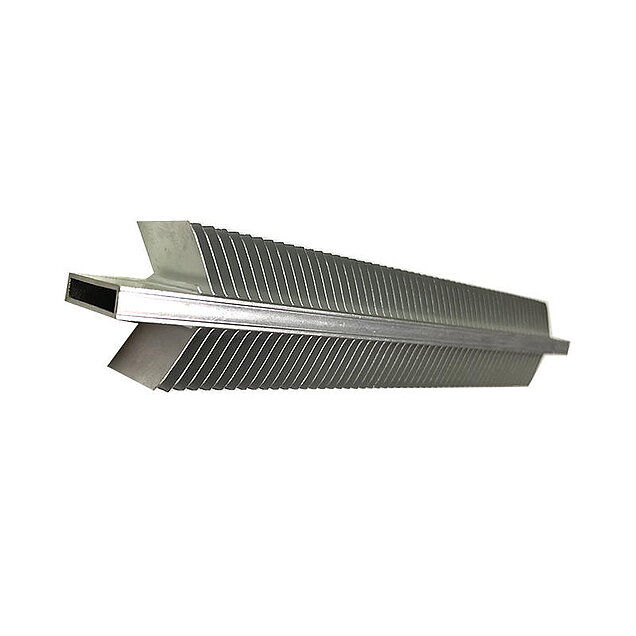


Single side and double side heat sink fin skiving
Special machine execution for double side fin skiving of heat sinks - flexible core heat exchanger tubes
Skived Heat Sink Benefits/Features
- Skived heatsink can be an alternative to extruded heat sink when looking for a fin density which can NOT be achieved by extrusion technology.
- Skived heatsink fabrication does not need expensive tooling which provides greater design flexibility. Instead, each fin is cut separately using the same tool which allows for lower tooling costs.
- Skiving heat sink can be made of copper and aluminum, enables solid copper solutions.The skiving process is a good thermal solution for high power cooling.
- Skived heat sink leading the heat innovation innovation high density ,high thermal performance, high aspect ratio, excellent performance.
- Skived heat sink without interface joint between the fins and base, improved thermal performance than traditional heat sink.
- Integrated manufacturing, no welding and mold opening;
- The thickness and spacing of fin can be made thinner and denser;
- The thermal conductivity is superior to the traditional extrusion and bonded fin process.
- High fin densities
- Perfect conductivity between base & fins
- Great forced airflow solution
- Low tooling cost
Skived Heat Sinks production cost compared to other type of heat sinks production

Benefits of a Skived fin Heat Sink
Aluminium extruded and die cast heat sinks dominate the industry. As devises that require cooling becoming smaller and heat generation increases, companies are forced to look for a more efficient cooling solutions. One of them is SKIVED FIN heat sinks.
Comparing Skived fin heat sink design to bonded fins type assembly, skived fins will outperform by large margin due to bonded assembly. Thermal transfer is somewhat reduced by the bonding agent added thermal resistance. There are five common techniques that are used to manufacture heat sinks out of one piece:
- Die Casting
- Machining
- Extrusion
- Forging
- Skiving Fins
Let’s discuss performance of each of those types of heat sinks:
Thermal Conductivity
Diecasting is a method for manufacturing complex shapes in high volumes and low cost. Initial tooling cost outlay is high, but the parts cost during the production run is relatively low. Drawback is porous structure as the molten aluminium alloy cools in the die-set it expands creating voids. The porous structure weakens the part and adds to thermal resistance to the heat sink.
Extruded aluminium alloy heat sinks are most cost effective way for manufacturing linear shapes. The drawback is the limitation in the freedom in design, but this method requires low cost tooling. During the extrusion, alloy is heated below melting point and force-feed thru the forming die-set. However the grain structure cannot be controlled evenly and shape of the heatsink cannot be optimized completely thus somewhat reduce thermal performance.
Machined heat sinks: This way of producing is due to high CNC machining costs of machined heat sinks, economically feasible only for prototyping and special low volume and high cost products. Cost of production is limiting this heat sinks to prototype production.
Forging is the most effective method to produce complex shapes in high quantity and also offers interesting thermal advantages due to processing alloys at room temperature. Due to the nature of the forging process, part is formed at high pressure and low temperature, process that allow better control of the grain structure. Making heat sinks stronger and better conductors of heat. See here for more info on this subject.
Skiving fins is the latest technology, which is very promissing and grows exponential due to the many benefits: heat sink is formed out of one block with the highest cooling capacity per weight of material.
Skived Fin Heat Sinks offer highly optimized cooling as they allow for higher fin densities than what is manufacturable using extrusion methodologies, but do not have an interface joint that restricts heat flow like bonded or brazed fin heat sinks. Unlike bonded or brazed heat sinks, Skived Fin Heat Sinks are constructed from a single piece of material and offer reduced thermal resistance since there is no joint between a base and fins. These heat sinks are manufactured by precisely slicing the top of the base, called skiving, folding it back to where it is perpendicular to the base, and repeating at regular intervals to create fins.
The skiving process enables high fin density and thin fin heat sink geometries for optimal thermal performance. By packing as much fin surface area into a given volume, skived fin heat sinks have greater heat transfer than other single piece construction heat sinks such as extruded aluminum heat sinks. Compared to extruded aluminum, skived fin heat sink fabrication does not rely on expensive tooling, providing greater design flexibility and faster prototyping. Instead, each fin is cut separately using the same tool which allows for lower tooling costs.
Skived heat sinks can be constructed of aluminum or copper allowing for full, one-piece copper solutions for high performance cooling.
The Skived fin process produces heat sink with 18% better thermal conductivity over extruded and 72% over die-cast part. Note that in this test average samples been tested. Best examples of each heat sink likely to produce better results somewhat dampening large outperformance by forged part.
Heatsink Surface Area
Increased surface area of the heat sink will yield lower thermal resistance and better component cooling, but only if boundary layer is not formed and fins close proximity do not prohibit flow of air. When designing extruded part, fins must be tapered so that the aluminium alloy will pass through the tool without breaking it. The number of fins in an extrusion limited by strength of the die set and the size of the extrusion. These restrictions have negative impact on the surface area.
Skived fins require also no taper for extraction from the die casted moulding tool, allowing for more fins per given heat sink size. The Skived fin heat sink increases the surface area by 21% without increasing the size compared to die cated parts. The result is improved thermal performance.
Reduced Cost
Depending on design, skived fin heat sink process can simplify manufacturing process. In cases when secondary operation required when working with extruded or die-cast heat sinks in skiving fins process this can be part of a single operation. That can greatly influence cost of the finished product. As the tooling cost is ZERO, this influence drastic the production cost!
Conclusion
Skived finheat sinks together with Forged heat sinks offer many advantages over machined, die cast and extruded processes. The improved thermal performance due to aluminium grain structure coupled with the increased surface area without increasing the size of the heat sink and low process cost are main advantages.
Skiving fins is also a very effective method for forming copper heat sink. Copper is difficult to extrude because it must be heated to high temperatures to soften the metal, making it challenging. Skiving is a cold process, and copper heat sinks can be formed with minimal waste.
PSF-Series - Fin Skiving Machines
3 models of High Precision production Skiving Machines: Hydraulic - NC/PLC - CNC controlled

Profimach PSFH - PLC driven
PLC Fin Skiving Machines
Hydraulic driven
3 SIZES skiving width:
140mm - 330 mm - 480 mm
Unlimited Lengths

Profimach PSFNC - NC driven
NC Fin Skiving Machines
Full step programmable
3 SIZES skiving width:
140mm - 330 mm - 480 mm
Unlimited Lengths

Profimach PSFCNC - CNC Driven
Full CNC programmable
3 SIZES skiving width:
140mm - 330 mm - 480 mm
Unlimited Lengths

Profimach PSFCNC-Flex- CNC driven
CNC Complex Fin Skiving Machines
full CNC control
2 SIZES skiving width:
400mm - 600 mm
table 300 x 800 mm - 600 x 1200mm
Profimach PSFNC/CNC - Fin Skiving Machines NC/CNC driven
3 SIZES : 140mm - 330 mm - 480 mm skiving width Unlimited Lengths

HIGH SPEED CNC controller
Powerful Controller with Mechatrolink Bus Protocol
SYNTEC/Mitsubishi MA controller comes with serial bus Mechatrolink connection motion control, improves machining performance by decreasing interpolation time and increasing surface’s smoothness. Serial bus communication control also improves traditional pulse delay of differentiate transfer time between axis, provides a simpler system and easier to install and setup.
Heat Sinks
Important Cooling Factors
Heat sinks maximize the surface of an object to be cooled for heat dissipation to the air. It sounds simple, but there are still many factors to consider! Housing, air speed and the materials used play an important role in the efficiency of the chosen cooling method. The thermal resistance of the material, the design of the cooling fins, the post-treatment, and even the color of the heat sink are factors which are decisive for the efficiency of the cooling, as well as the attachment of the heat sink.
Thermal resistance
The cooling capacity of the heat sink. The lower the resistance, the higher the cooling capacity.
Cooling Material
The material used partly determines the extent of thermal conductivity. Copper and aluminum are the most widely used materials, though aluminum is the more common choice because copper is more expensive and heavier. Aluminum 6061 and 6063 are widely used with a thermal resistance of 166 and 201 W / mK, respectively.
In comparison
- Copper: 385 W / mK
- Iron: 55 W / mK
- Tin: 50W/mK
- Steel: 36 W / mK
- Glass: 0.8W/mK
- Air: 0.025W/mK
- Die-casted aluminum materials, from 80 to 100 W/mK
- Thermo-plastic materials, from 3 to 25 W/mK
The design of the fins
The shape and positioning of the fins have a significant impact on performance levels. The fins should, for instance, not be placed too close to one another when air flow is minimal, as that would slow the air flow down too much.
Post-treatment and colour
Post-treatment and colour of the cooling surface determine the level of heat radiation, and a particularly low amount of convection plays an important role in the final output. Heat sinks are often anodised. This process improves on a chemical level the heat radiation of the surface. In most cases a black colour provides the best level of performance
Skived wavy fins heat sink: Waved fins after fin skiving with serrated knife.
Heat dissipation surface increases with 8 to 15%. Highest heat dissipation per weight of heat sink
More information on Fin Skiving Machines: Click Here
www.finskiving.com
www.finskiving.com
Heat Sinks
Which heat sink to chose??
Extruded Heat Sinks
Extruded heat sinks are the most common heat sinks used for thermal management. Extruded heat sinks are generally used in medium power systems both in natural and forced convection. The extrusion process, pushing hot raw aluminium through a steel extrusion die to create the desired profile allows for innumerable complex shapes to be manufactured. Many standard shapes are available but modifying the profile shape changes the surface in contact with the air and consequently the heat dissipation capability. Columbia-Staver can supply standard profiles or engineer a heat sink shape to achieve optimal performance in the space available. After cooling and ageing, the material is cut to the final heat sink length and any additional features such as holes or pockets can be added.
Extruded heat sinks can be supplied raw or with a finish, such as anodizing, electrophoresis or powder coating. Certain finishes can alter the emissivity, which can enhance thermal performance.
Cold Forging
Cold forging is a cold working process. Aluminium is squeezed by a press into the closed die, the resultant heat sink taking on the shape of the void in the die. This process is also known as cold heading. Cold forged heat sinks often have high performance compared with other technologies, mainly because any increase to the surface area of a heat sink will almost always result in improved thermal performance. Forged fins can be made almost perfectly straight, allowing for more fins per square inch than in an extruded product. The part is formed under high pressure which controls the grain structure and results in improved thermal performance The fins can also be formed into an elliptical or circular shape enabling airflow from any direction – a big advantage in some applications.
Stacked, Zipper, Folded Fin Heat Sinks
Stacked or zipper fin heat sinks can be an alternative to both extrusion and skived when looking for high density structure. Unlike the one piece skived fin heat sink, a zipper fin heat sink is an assembly of a base and a separate fin stack. The fin stack is created using a set of individually stamped fins, these fins are stacked or “zipped” together to form a block of fins. The finished fin stack is then soldered or bonded to the heat sink base. Zipper fins are most often used with a base plate but they can also be used with heat pipes. A hole or holes are stamped into the fins and the fin stack set is placed on a series of heat pipes to form the heat sink. Zipper fins can be manufactured from either copper or aluminium. Zipper fin heat sinks can also be customized with heat pipes embedded into the base plate to enhance performance.
Skived Heat Sinks
Skived fin heat sinks can be used as an alternative to extruded heat sinks when looking for a fin density which can’t be achieved by extrusion technology. Skived heat sinks can be manufactured from either copper or aluminium and usually have 0.5mm thick fins, although fins as thin as 0.2mm are achievable. In this manufacturing technology the heat sink fins are literally carved out of the base of the Heat sink. In the machine, specially designed blades slice the surface cutting very fine and thin fins into the raw metal block at a shallow angle, the fins are then folded vertically and aligned with the previous fin. As the fins and the heat sink base are part of the same block of material, skived fin heat sinks give excellent thermal conductivity between fin and base. Skived heat sinks can also be customized with embedded heat pipes to enhance performance if required.
Die-Cast Heat Sinks
Die casting is the process of injecting liquid metal under high pressure into a high precision mould created using two hardened tool steel dies. One of the big advantages of die casting is that it is an effective method of forming complex shapes of high tolerance with little need for post moulding machining. Mounting holes, slots, pins etc can be added with little cost penalty.
Heat sinks can be die-cast in both aluminium and zinc materials, however the thermal conductivity of the Die Cast material is not as good as that used in extruded heat sinks and die casting tooling is generally more expensive than extrusion tooling. A variety of surface treatment options are available depending on the casting material these include anodising, electrophoresis and powder coating.
INFO on Cold forming Extruded Heat Sink production
Heat Sink Cold forging machines - Heat sink cold forming machines
Get more info on the cold forming heat sink extrusion machines
Fin skiving machine , heatsink fin skiving machine , metal skiving machine , skived fin heatsink, copper skived fins, aluminium skived fins, skived heatsinks, skived fin, fin skiving machine, skiving machine, cnc skiving machine, mechanic skiving machine, hydraulic skiving machine, heatsink scarfing machine, scarfing heatsinks, Fabrication for High Fin Density Heat Sinks, Skiving machine. Skiving or scarfing machines, metal skiving machine, metal skarving machine,Fin skiving Machine for high performance heat sink production Fin skiving machine - heat sink fin skiving machine - metal skiving machine - Skiving Fin Heatsinks Machine For Aluminium - Skiving Fin Heatsinks Machine For copper






