Precision Fin Skiving
Highest performing heat sinks at lower cost
Skiving heat sink manufacturing technogy is a unique metal forming process, most widely used copper and aluminium heat sink integrated forming process.
"Precision Skiving" is not known from where, just from the name of the hard to imagine the actual processing technology, but with the name Skiving, it is easy to understand.
Skiving, skive, means to slice. Processing method: according to the needs of a whole piece of metal profile.
Using a special planer with precise control, thin slices of specified thickness are cut and then bent upward into an upright state to become heat dissipation fins.
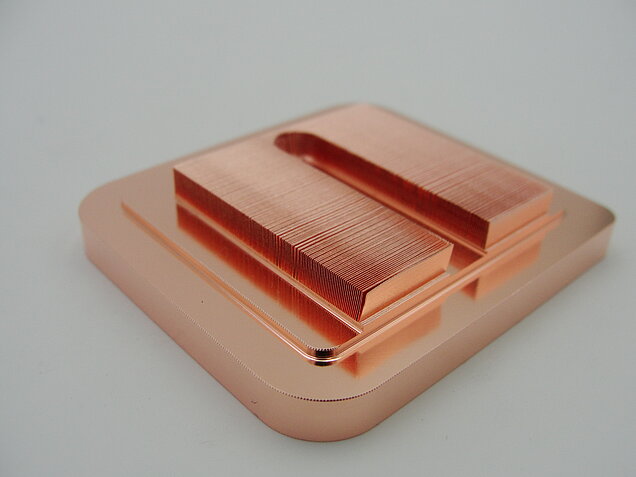

Skived fin heat sinks are made from raw metal block where fins are literally carved out of the heat sink base by a special blade tool. Since both fins and base are shaped from a single piece of raw metal block, skived fin heat sink are considered to be the best thermal conductivity between fins and base. Skiving method typically is used for aluminum and copper heat sink. Although it could be more costly than extrusion, skiving method is an ideal manufacturing method for prototyping and high performance applications.
More information on Fin Skiving Machines: Click Here
www.finskiving.com
www.finskiving.com
Website fully dedicated to Heat Sink Fin skiving
How to Produce Heat Sinks With Skiving
Production of Skived Heat Sinks
For the production of skived heat sinks, a solid block of aluminum or copper, having a certain thickness, is used as a starting material. The block is extruded in a rectangular shape. It is then placed on a worktable. Lubricant is applied to the top of the surface so that excessive heat is not generated during the machining process. The block is then passed through a machine that consists of a sharp blade. The blade slices the top of a block to the desired thickness and bends the slices.
This slicing process is repeated at certain intervals to make a series of fins along the length of the block and to attain the designated spacing between them.
Materials Used for the Production of skived fin heat sinks
1. Copper Skived fin heatsink: Copper (mostly used Copper C11000) thermal conductivity is good, plus the skived fin technology can achieve the maximum heat dissipation area per unit volume, greatly improve the overall heat dissipation performance. So copper skived fin heat sink is used in high end chip, cpu heat dissipation, server and other fields. Skived copper heat sinks offer the maximum heat dissipation in applications that have high airflow and small space. The thermal conductivity of copper (~400 W/m-K) is the highest among all the commercial metals, and the skiving technology allows the heat sinks to have very thin fins, high aspect ratio and high fin density. Because the fins are an integral part of the base, skived copper heat sinks provide the best possible thermal conductivity between the fins and the base. When optimized to specific applications, skived copper heat sinks offer outstanding performance over any other thermal solutions within the small space. In some applications, the skiving technology is also the most cost-effective and reliable method of producing heat sinks that meet high thermal demands.
2. Aluminum skived fin heat sink: Generally made of pure aluminum, thermal conductivity is higher than aluminum alloy, and with skiving technology, heat dissipation performance is more stable than aluminum extrusion heat sink. Aluminum skived heat sink widely used in photovoltaic industry, electric vehicles, inverters, led lights ,communication products and so on. The preferred aluminium material for the manufacturing of heat sink through the skiving process is Aluminum 6063. The reason is that the machinability of this material is better and it has relatively higher strength. Also, the range of fin thickness can lie between 0.08 – 2.8mm. This results in the production of fins which are quite thin, having a lightweight. This manufacturing process can produce fins of height up to 150mm.
Evaluation of skiving fins
For this kind of manufacturing process for a heat sink, the major advantage is that there are no metal chips or wastage produced and in this process as the block of metal is only sheared into layers. Originally, skiving was used to produce thin natural convection arrays, but recent research has helped to attain a closer spacing between the fins which is necessary for forced convection cooling.
Advantages of Creating Heat Sinks With Skiving
Fins can offer maximum dissipation of heat in the application where there is a very high flow of air and space is limited. In other heat sinks, fins may be bonded separately to metal sheets with different methods like welding and epoxy resins. However, joining the fins with the base takes time and it costs since more equipment and labor is required. When it comes to skiving, joining pieces of metal is not required since the entire heat sink is made out of a single piece of metal. Another advantage is that there is not any additional thermal resistance that affects the performance of a heat sink. This allows optimal cooling performance in the environment where the skiving heat sink is installed.
Heat sinks produced with skiving have a very high aspect ratio, which reduces the weight of heat sinks. The tooling cost is minimal as only a sharp blade is used. Another advantage is that the lead time of the skiving process is very short as only slicing and bending operation is required to produce a final product. This allows the production of a large number of heat sinks in a relatively shorter time.
Limitation of Skiving
The biggest limitation of a skiving heat sink is that the magnitude of force required to shear the metal block into thin slices and to bend them is very large. This applied force depends upon the flow length of the blade, the thickness of layers and the height of the fins.
Additional Machinery Needed for the Process
The starting metal block used in skiving for creating heat sinks has a very large length to reduce the lead time. To attain the designated length, the block of a skived heat sink is passed through a gear cutting machine which cuts the heat sink into several parts of the desired length. During this process, some burrs and sharp corners are formed at the ends of the fins. In order to remove those burrs and sharp corners, heat sinks are passed through a grinding machine. The tool is a gear generated grinder which removes the burrs and sharp corners. This process also smooths the surface of the heat sink and controls the height of the final product.
Applications of Heat Sinks Produced with Skiving
Skived heat sinks have vast applications. They can allow maximum dissipation of heat in a very limited space as they have a very large surface area to volume ratio due to large packing density. Skived heat sinks are most commonly used in the following applications:
- Automotive components
- Industrial components and equipment
- Electronic equipment like transistors and light-emitting diodes
- Computer equipment like GPU
- Household appliances and lighting lamps
- Satellite and Telecommunication
- Computer and electronic component
- Telecommunication equipment
- LED Lighting and household appliances industry
- 5g base station and server

Skived Fin Heat Sinks offer highly optimized cooling as they allow for higher fin densities than what is manufacturable using extrusion methodologies, but do not have an interface joint that restricts heat flow like bonded or brazed fin heat sinks. Unlike bonded or brazed heat sinks, Skived Fin Heat Sinks are constructed from a single piece of material and offer reduced thermal resistance since there is no joint between a base and fins. These heat sinks are manufactured by precisely slicing the top of the base, called skiving, folding it back to where it is perpendicular to the base, and repeating at regular intervals to create fins.
The skiving process enables high fin density and thin fin heat sink geometries for optimal thermal performance. By packing as much fin surface area into a given volume, skived fin heat sinks have greater heat transfer than other single piece construction heat sinks such as extruded aluminum heat sinks. Compared to extruded aluminum, skived fin heat sink fabrication does not rely on expensive tooling, providing greater design flexibility and faster prototyping. Instead, each fin is cut separately using the same tool which allows for lower tooling costs. This enables you to fully customize skived fin components for your product, which also includes liquid cooling applications.
Skived heat sinks can be constructed of aluminum or copper allowing for full, one-piece copper solutions for high performance cooling.
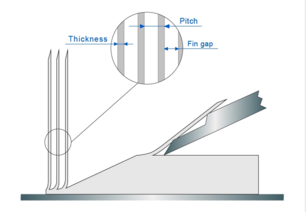
How to identify a Skived Heat sink
It is fairly easy to identify a Skived Heat sink as the heat sink has a curve where the blade finishes its cut at the base of the heatsink as shown in the picture. In addition, the fins are not completely vertical, and curve slightly. This is more pronounced at the fins get taller. Typical width of the plate fin is 150/320/500 mm, but it is possible to manufacture up to 600 mm wide heatsinks. As a Skived heatsink is manufactured from a long block of material, the only is no real limit to length of the heatsink is the length of the block. Different heights can be achieved by machining the block of material. Any excess material is recycled to reduce wastage. Typical Finishes for Aluminum skived heatsink are Anodization, or Nickel Plated. Typical finished for Copper Skived heatsinks are Anti-Oxidant, or Nickel Plated.
More information on Fin Skiving Machines: Click Here
www.finskiving.com
www.finskiving.com
General Design Guidelines for Skiving
- Aluminum is a better material for high aspect ratios.
- There has to be some trade-off between different dimensional variables like thickness and height of fin due to the complexity of the manufacturing process.
- There is a limitation of airflow lengths due to the force required to fold up the fins.
Final Thoughts
This method of creating heat sinks becomes increasingly more popular. It guarantees the best performance and a low production cost. Skived heat sink will be more widely used, skived fin process can also cooperate with other cooling process in production, such as the heat pipe technology, also can match the water cooled heat sink process, micro channel and so on. According to the characteristics demanded, it is possible to produce skived fin heat sinks in different shapes and sizes, with an improved heat sink performance, at the same time with reduced cost. Skiving operation has requirements for the used material who are not high.
Skived heat sink is a cost effective solution when considering the low tooling cost and the optimized fin surface area