DEFINITION OF ROLLING
The rolling process consists of a technique of deformation of metal surfaces by means of a strong pressure exerted by hardened steel rollers with the aid of high precision mechanisms
The result of the rolling process is a solid and hardened finish, but above all perfectly smooth. Modern rolling equipment works at a very high level of preset precision, to ensure absolutely perfect results
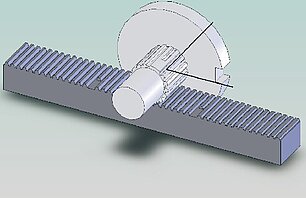
Spline rolling is one of the most popular and economical manufacturing processes for creating an involute tooth form. This cold forming process offers many advantages in the manufacture of automotive and power transmission shafts, motor shafts, pump shafts, axles and other parts where there is a need to transmit torque. Global manufacturers count on spline rolling for its ability to produce splines, grooves, and threads at production rates of up to 300 parts per hour.
Simply put, spline rolling uses paired racks mounted in a spline rolling machine to roll highly complex geometric shapes into metal parts between centers. Many shafts are turned between centers with a face driver, and then have the splines rolled between centers. Both processes are between centers resulting in superior parts produced at a lower per piece cost when compared to more traditional methods.

Why Spline Rolling?
Versatility
The terms “spline rolling” and “cold forming” are used interchangeably but the process can produce far more than spline geometries. Examples include: helicals, threads, snap-rings, worms, spurs, tapered, oil grooves, pinions, and burnishing. Cold forming can also be used to generate sheet-metal parts. Multiple pairs of racks can be utilized in the same stroke, allowing multiple geometries to be rolled on a single part in a single machine cycle.
Strength, Finish, Precision
Spline rolling forms part geometries by forcing, and controlling, material “displacement.” Extreme forces are exerted on the part by the rack. At high enough pressure the part’s metal flows between the rack teeth. Displacement offers numerous benefits. The flowing metal is carefully controlled by the geometry of the rack offering unmatched accuracy and repeatability. Displacement also work-hardens the surface of the rolled part offering up to 40% greater load-carrying characteristics. Lastly, the controlled displacement results in a finer surface finish, offering improved fit characteristics, less backlash and better overall assembly longevity and performance.
Horizontal machines are all "wide mold " machines
Orientation function of spline rolling
Oriented spline rolling function - incomplete teeth spline rolling function
It has the special function that the workpiece needs to be oriented or has incomplete teeth.
Unique forming principle and precise positioning mechanism can process the spline to the nearest of the shoulder, no need to retract the tool
Mold Clamping Module
Combined functions of mold clamping module
The accurate mold clamping module makes the mold replacement easy and fast, without the need for tooth alignment.
Variety of combined functions of mold clamping module possible: all horizontal machines are "WIDE MOLD" Machines, which give multi-combined tooling posibilities. You can Roll different surfaces in one time passing
LATEST TECHNOLOGY FOR SPLINE ROLLING ON HOLLOW SHAFTS
In order to reduce weight, hollow shafts are increasingly being used in drive train systems. So far, such shafts could only be splined with the conventional cross rolling process up to a certain minimum wall thickness. In case of extremely thin-walled workpieces, more cost-intensive spline manufacturing processes had to be planned. With our newly developed reverse rolling process, the forming process itself takes a bit longer. But it´s possible to form splines on hollow shafts with wall thicknesses of up to less than 3 mm.
In the case of partial hollow shafts, processes can also be combined appropriately in order to achieve the most ecconomic cost-effectiveness.
Advantages and disadvantages of thread rolling
Thread rolling is usually performed on a thread rolling machine or reeling machine.
Forming rolling molds deform plastically workpieces to obtain threading surface.
Advantages
1 The surface roughness is less than turning, milling and grinding;
2 After rolling, the surface of the thread can be hardened to improve the strength and hardness;
3 high material utilization rate;
4 Productivity has grown exponentially over cutting, and is easy to automate;
5 rolling die life is very long.
Disadvantages
1.However, the rolling thread requires that the hardness of the workpiece material does not exceed HRC40;
2.the dimensional accuracy of the blank is required to be high;
3.the precision and hardness of the rolling die are also required to be high, and the manufacture of the die is difficult;
4.and it is not suitable for asymmetric thread rolling.

